/Physical Oceanography/Temperature
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
Resolution
-
Advanced Along-Track Scanning Radiometer multimission data have been reprocessed to provide update retrievals of Sea Surface Temperature (SST) to produce the AATSR Reprocessing for Climate (ARC) dataset.
-
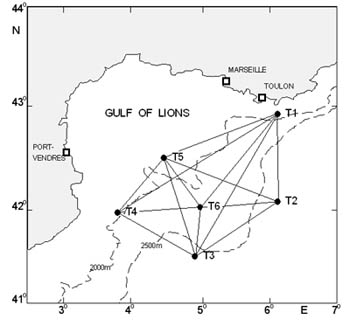
The acoustic tomography approach provides an indirect measure of the temperature of an ocean volume. The technique provides an integrated measure of temperature along the sound propagation paths. The variety of paths between a transmitter and a receiver, as well as the large number of instruments deliver information on the variability of the thermal content of the insonified volume.
-
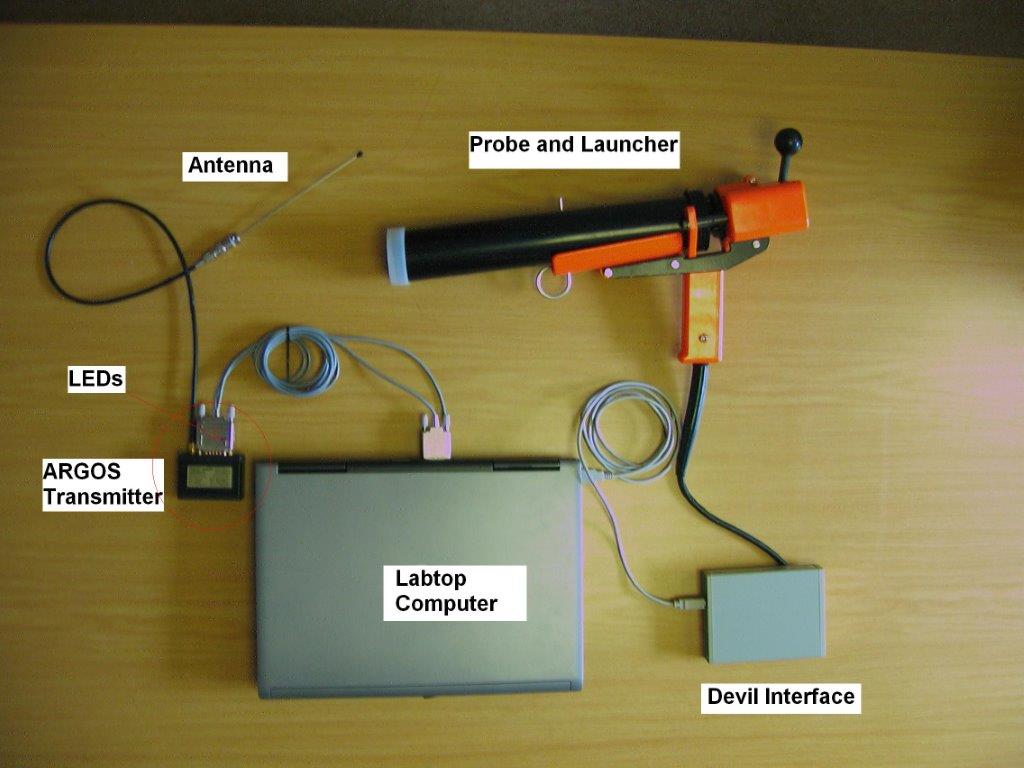
X : eXpendable; B : Bathy; T: Thermograph. Thermal profile measurement with real-time transmission
-
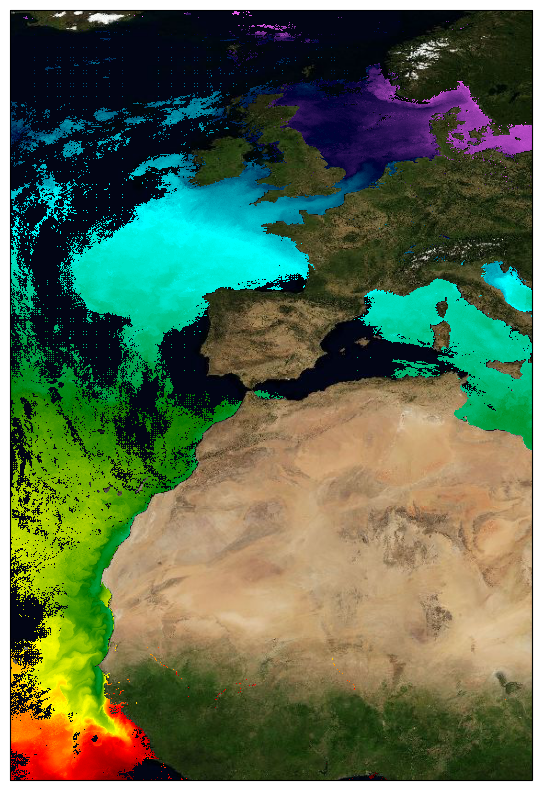
This dataset provide a times series of daily multi-sensor composite fields of Sea Surface Temperature (SST) foundation at ultra high resolution (UHR) on a 0.02 x 0.02 degree grid (approximately 2 x 2 km) for the North-East Atlantic (European North West shelf, Iberia, Bay of Biscay, Irish Sea down to Canary upwelling), every 24 hours. Whereas along swath observation data essentially represent the skin or sub-skin SST, the L3S SST product is defined to represent the SST foundation (SSTfnd). SSTfnd is defined within GHRSST as the temperature at the base of the diurnal thermocline. It is so named because it represents the foundation temperature on which the diurnal thermocline develops during the day. SSTfnd changes only gradually along with the upper layer of the ocean, and by definition it is independent of skin SST fluctuations due to wind- and radiation-dependent diurnal stratification or skin layer response. It is therefore updated at intervals of 24 hrs. SSTfnd corresponds to the temperature of the upper mixed layer which is the part of the ocean represented by the top-most layer of grid cells in most numerical ocean models. It is never observed directly by satellites, but it comes closest to being detected by infrared and microwave radiometers during the night, when the previous day's diurnal stratification can be assumed to have decayed. The processing combines the observations of multiple polar orbiting and geostationary satellites, embedding infrared of microwave radiometers. All these sources are intercalibrated with each other before merging. A ranking procedure is used to select the best sensor observation for each grid point. The processing is described on Copernicus Marine Service [SST_ATL_PHY_L3S_NRT_010_037 dataset] and users can refer to the user manual and quality documents available there for more details. This dataset is generated daily within a 24 delay and is therefore suitable for assimilation into operational models. It is produced in the frame of Copernicus Marine Service and the data available through various tools and protocols with a simple user registration from this service (product identifier: SST_ATL_PHY_L3S_NRT_010_037) at: https://data.marine.copernicus.eu/product/SST_ATL_PHY_L3S_NRT_010_037/
-
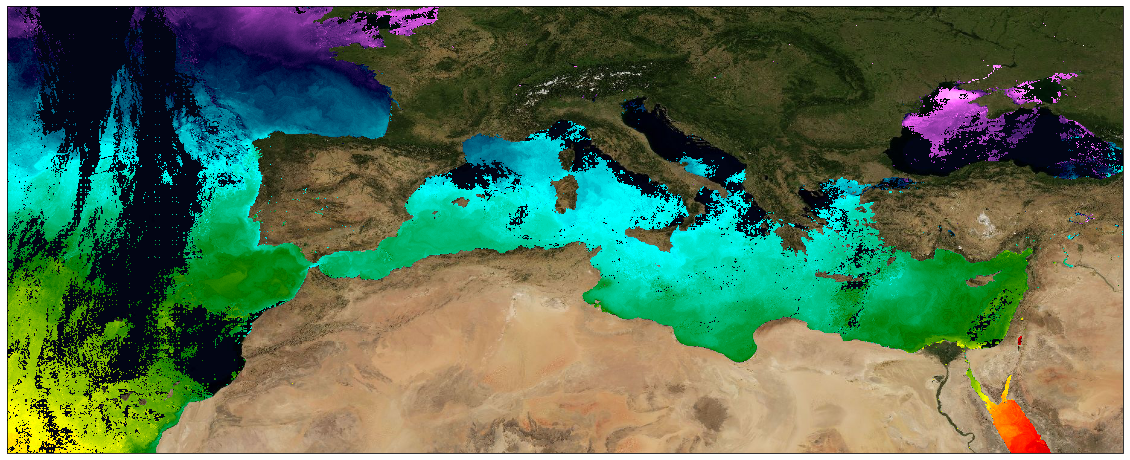

This dataset provide a times series of daily multi-sensor composite fields of Sea Surface Temperature (SST) foundation at ultra high resolution (UHR) on a 0.02 x 0.02 degree grid (approximately 2 x 2 km) over Mediterranean Sea, every 24 hours. Whereas along swath observation data essentially represent the skin or sub-skin SST, the L3S SST product is defined to represent the SST foundation (SSTfnd). SSTfnd is defined within GHRSST as the temperature at the base of the diurnal thermocline. It is so named because it represents the foundation temperature on which the diurnal thermocline develops during the day. SSTfnd changes only gradually along with the upper layer of the ocean, and by definition it is independent of skin SST fluctuations due to wind- and radiation-dependent diurnal stratification or skin layer response. It is therefore updated at intervals of 24 hrs. SSTfnd corresponds to the temperature of the upper mixed layer which is the part of the ocean represented by the top-most layer of grid cells in most numerical ocean models. It is never observed directly by satellites, but it comes closest to being detected by infrared and microwave radiometers during the night, when the previous day's diurnal stratification can be assumed to have decayed. The processing combines the observations of multiple polar orbiting and geostationary satellites, embedding infrared of microwave radiometers. All these sources are intercalibrated with each other before merging. A ranking procedure is used to select the best sensor observation for each grid point. The processing is the same (minus the optimal interpolation step) as for the Atlantic Near Real Time (NRT) L3S dataset available on Copernicus Marine Service [SST_ATL_PHY_L3S_NRT_010_037 dataset] and users can refer to the user manual and quality information documents available there for more details. This dataset is generated daily within a 24 delay and is therefore suitable for assimilation into operational models.
-

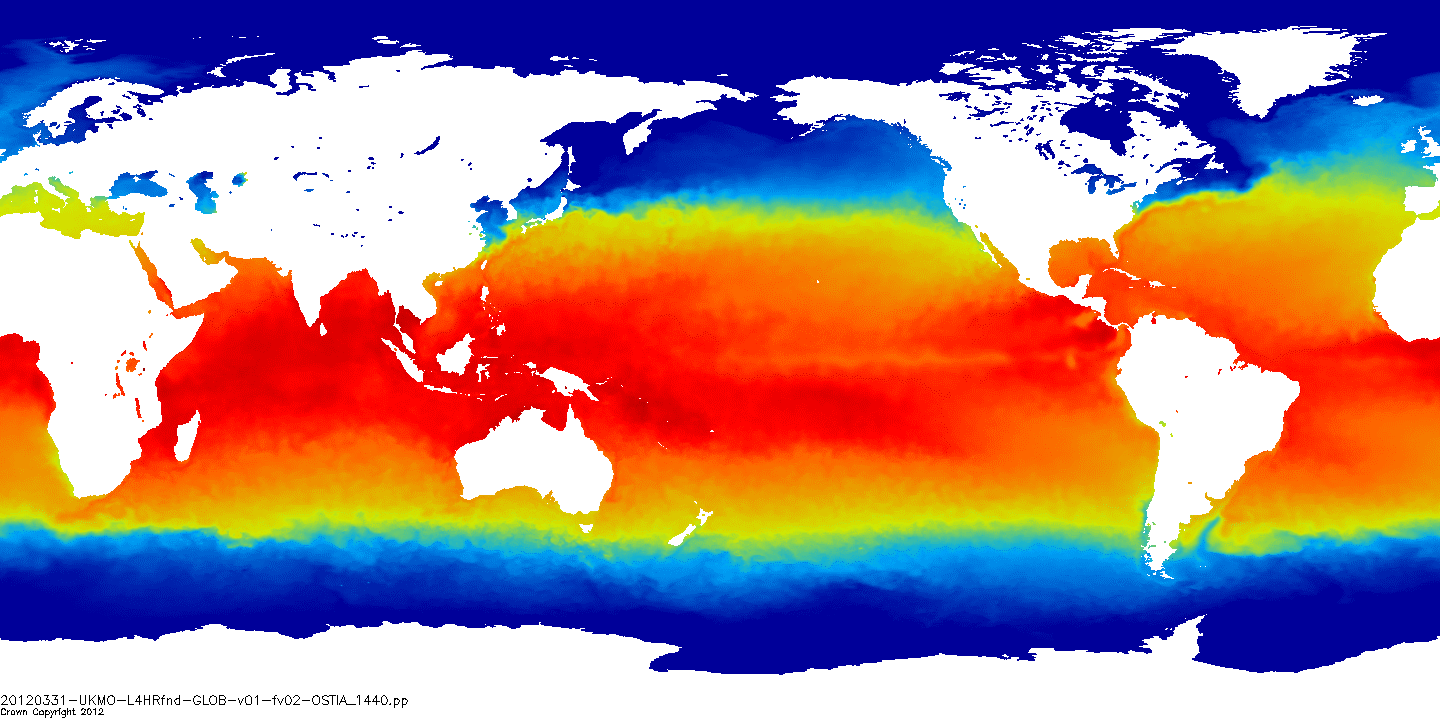
This dataset provide a times series of daily mean fields of Sea Surface Temperature (SST) foundation at high resolution (UHR) on a 0.10 x 0.10 degree grid (approximately 10 x 10 km) for the Global Ocean, every 24 hours. An Optimal interpolation (OI) technique is used to combine coincident swath measures of SST from different types satellite sensors and to fill gaps where no observations are available or obstructed by clouds. This multi-sensor compositing and interpolation process categorizes this dataset as a Level 4 product. Each daily mean field is available the next day before 12:00. Whereas along swath observation data essentially represent the skin or sub-skin SST, the L4 SST product is defined to represent the SST foundation (SSTfnd). SSTfnd is defined within GHRSST-PP as the temperature at the base of the diurnal thermocline. It is so named because it represents the foundation temperature on which the diurnal thermocline develops during the day. SSTfnd changes only gradually along with the upper layer of the ocean, and by definition it is independent of skin SST fluctuations due to wind- and radiation-dependent diurnal stratification or skin layer response. It is therefore updated at intervals of 24 hrs. SSTfnd corresponds to the temperature of the upper mixed layer which is the part of the ocean represented by the top-most layer of grid cells in most numerical ocean models. It is never observed directly by satellites, but it comes closest to being detected by infrared and microwave radiometers during the night, when the previous day's diurnal stratification can be assumed to have decayed. The processing combines the observations of multiple polar orbiting and geostationary satellites, embedding infrared of microwave radiometers. All these sources are intercalibrated with eachother before merging. This dataset is generated daily within a 24 delay and is therefore suitable for assimilation into operational models. It is produced in the frame of Copernicus Marine Service and the data available through various tools and protocols with a simple user registration from this service (product identifier: SST_GLO_PHY_L4_NRT_010_043) at: https://data.marine.copernicus.eu/product/SST_GLO_PHY_L4_NRT_010_043
-
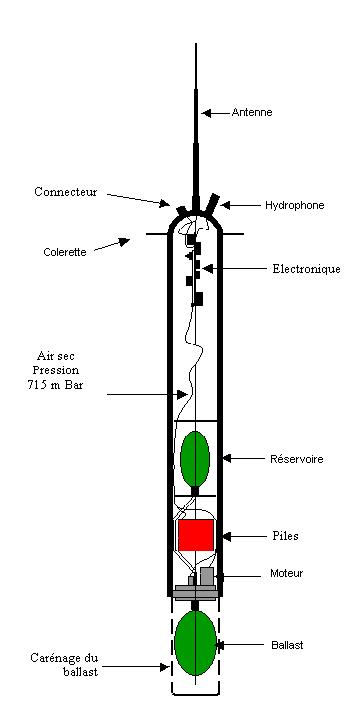
The RAFOS float technique (the reverse acronym of SOund Fixing And Ranging) is used to obtain sub-surface trajectories of floats by acoustic location. These floats are immersed at a constant depth and drift with the body of water in which they are immersed. The floats record the arrival time of the sound signals emitted by a network of fixed acoustic sources placed on moorings. They regularly come to the surface to transmit the data that they have recorded.
-
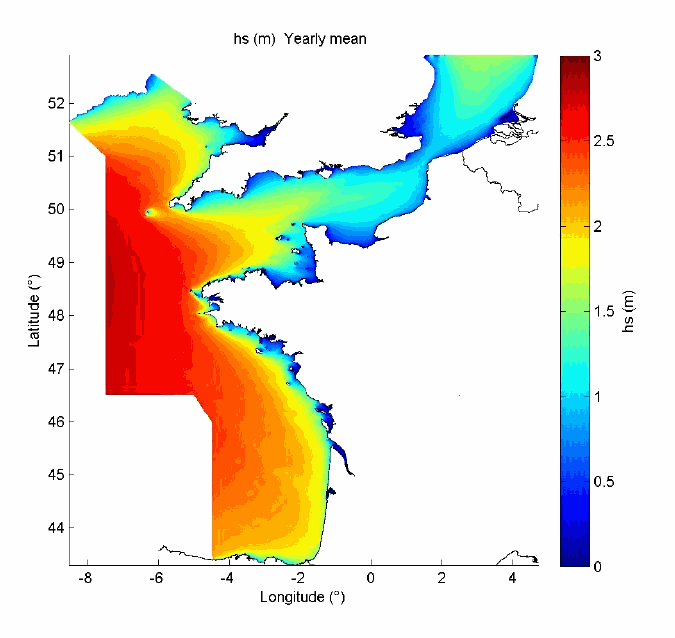
-
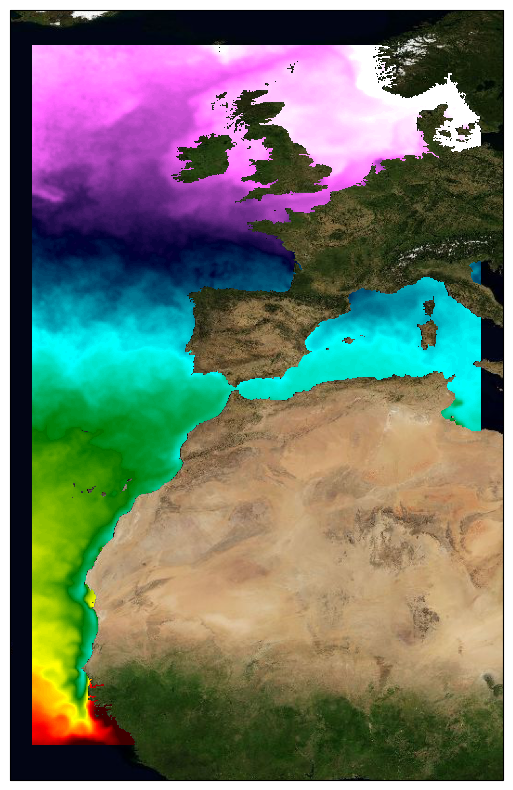
This dataset provide a times series of daily multi-sensor composite fields of Sea Surface Temperature (SST) foundation at ultra-high resolution (HR) on a 0.02 x 0.02 degree grid (approximately 2 x 2 km) for the North East Atlantic, every 24 hours. An Optimal interpolation (OI) technique is used to combine coincident swath measures of SST from different types satellite sensors and to fill gaps where no observations are available or obstructed by clouds. This multi-sensor compositing and interpolation process categorizes this dataset as a Level 4 product. Each daily mean field is available the next day before 12:00. Whereas along swath observation data essentially represent the skin or sub-skin SST, the L3S SST product is defined to represent the SST foundation (SSTfnd). SSTfnd is defined within GHRSST as the temperature at the base of the diurnal thermocline. It is so named because it represents the foundation temperature on which the diurnal thermocline develops during the day. SSTfnd changes only gradually along with the upper layer of the ocean, and by definition it is independent of skin SST fluctuations due to wind- and radiation-dependent diurnal stratification or skin layer response. It is therefore updated at intervals of 24 hrs. SSTfnd corresponds to the temperature of the upper mixed layer which is the part of the ocean represented by the top-most layer of grid cells in most numerical ocean models. It is never observed directly by satellites, but it comes closest to being detected by infrared and microwave radiometers during the night, when the previous day's diurnal stratification can be assumed to have decayed. The processing combines the observations of multiple polar orbiting and geostationary satellites, embedding infrared of microwave radiometers. All these sources are intercalibrated with eachother before merging. This dataset is generated daily within a 24 delay and is therefore suitable for assimilation into operational models. It is produced in the frame of Copernicus Marine Service and the data available through various tools and protocols with a simple user registration from this service (product identifier: SST_ATL_SST_L4_NRT_OBSERVATIONS_010_025) at: https://data.marine.copernicus.eu/product/SST_ATL_SST_L4_NRT_OBSERVATIONS_010_025/
-
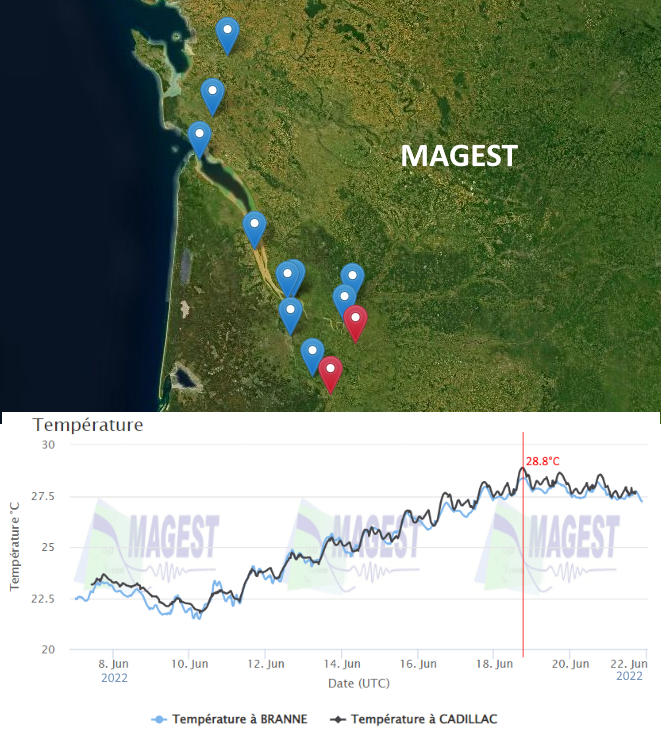
The MAGEST observation network aims to continuously monitor the physico-chemical quality of the waters of the estuaries of Northern Aquitaine. In 2023, this regional network is composed of 12 stations.
 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA